总结学习 React 以及相关生态时遇到的难点以及重点
基础知识点
-
单向数据流(子组件不能修改父组件数据)
-
组件名首字母大写
-
可以使用
<React.Fragment></ React.Fragment>或者<></>包裹标签 -
关键字
class->className<label for="id名"></lable>-><label htmlFor="id名"></lable>用来扩大点击范围
-
不要直接修改
state要使用this.setState() -
this指向问题// 在constructor使用bind,无法传参数
this.handlerClick = this.handlerClick.bind(this);
// 调用时使用bind,对性能优化不友好,因为每次render()时都要重新bind
onChange={this.handlerClick.bind(this,num)}// 使用箭头函数
onChange={e => this.handlerClick(num)}// 声明为箭头函数,无法传参
handlerClick = num => {}; -
循环渲染加 key,不要使用 index 作为 key 值。
-
注释写法
{/\*\*/} -
dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{__html: item(需要展示的数据)}} // 不转义html标签 -
setState()第二个参数为回调函数
-
一旦
state,props变化,render()就会执行。也就是说一旦父组件 state 变化时,render()会执行所以其父组件的中的子组件也会再render()一遍。 -
当组件中只有
render()时,可以把它声明成一个无状态组件,可以提升性能 -
ref 用来获取 dom 元素,
ref={(element) => {}}element 为该元素
组件通信
父->子
通过属性传递,子组件通过 this.props 接受,父组件值的改变会直接影响到子组件。
父组件
// 父组件中使用子组件
const name = 'Alan'
<Child name={name} />
子组件
<div>{this.props.name}</div>
子-> 父
父组件将自己方法传递给子组件,子组件通过添加事件来调用该方法。这样就可以达到子组件修改父组件数据的目的,同时可以将子组件的数据传递给父组件。
父组件
this.state = {
list: [1,2,3]
}
<Child handlerEvent={this.deleteItem.bind(this)} />
// 方法
deleteItem(index) {
const list = [...this.state.list];
list.splice(index,1);
this.setState({
list,
});
}
子组件
<button onClick={() => this.props.handlerEvent(1)}></button>
props 参数校验及默认值
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
// 参数校验
// Child为组件名
// 定义this.props.content为string类型并且为必须参数
Child.propTypes = {
content: PropTypes.string.isRequired
};
// 参数默认值
Child.defaultProps = {
mobile: 'none'
};
异步组件加载插件react-loadable
使用方式
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Loadable from 'react-loadable';
const LoadableComponent = Loadable({
// 需要异步引入的组件
loader: () => import('./index'),
loading() {
// 加载时进行的操作,这里显示loading提升用户体验
return <div>loading...</div>;
}
});
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return <LoadableComponent />;
}
}
虚拟 DOM
何为虚拟 DOM
使用 JS 对象来描述真实 DOM,虚拟 DOM(JS 对象)的操作性能要远远优于真实 DOM 操作性能。
通过 React.createElement(type, [props], [...children]) 来生成虚拟 DOM
优点:
-
DOM 操作很耗性能,虚拟 DOM 操作性能好
-
无需替换全部 DOM,通过 diff 算法比对替换局部改变的 DOM
-
由于使用了虚拟 DOM,有利于原生应用的开发(RN),因为 DOM 是存在于浏览器中的。
出于性能考虑,react 将多次 setState(异步函数)合并成一次 setState,因为 setState 会导致虚拟 DOM 进行 diff 对比。
diff 算法
生命周期
- mounting
componentWillMount/UNSAFE_componentWillMountrender()componentDidMount应用场景:发送请求
- updation(props/state 发生变化)
componentWillReceiveProps()将废除shouldComponentUpdate更新之前,返回 true 时才会更新render()componentDidUpdate
- unmounting
componentWillUnmount
性能优化
// 只有当子组件数据变化时才去执行render()
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return nextProps.content !== this.props.content;
// 防止更新影响性能
}
也可以使用组件去继承 React.PureComponent 以达到和上面一样的效果,但是应该减少使用,因为它存在一些问题。问题
在 hook 中也有类似的 API:useMemo 和 useCallback
useMemo 参考资料:
Redux
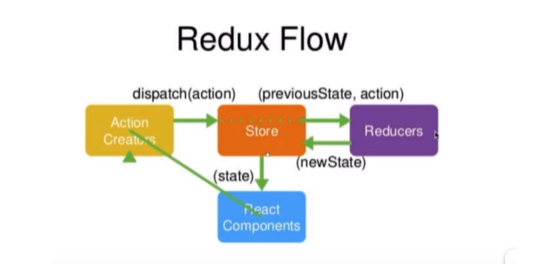
原理
组件通过 dispatch(action) 来通知 store , store 根据 action 来调用对应的 reducers 来操作 store 副本, reducers 将处理好的数据返回给 store 。
store 和组件之间通过,store.subscribe(this.setState(store.getState())) 来同步最新的 store 数据。
- 创建 store (createStore())
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import reducer from './reducer';
// 第二个参数配置后可以使用谷歌redux插件
const store = createStore(
reducer,
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
);
export default store;
- 创建 reducer(管理操作数据 store 副本)
const defaultState = {
todoText: ''
};
export default (state = defaultState, action) => {
if (action.type === 'action的type') {
let newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state));
// 更新store
newState.todoText = action.value;
return newState;
}
return state;
};
可以通过 store.getState() 来获取 store 中的数据,给组件赋初值
this.state = store.getState();
- 创建 action
const action = {
type: '',
value: '' // 要改变的值
};
- 通过
store.dispatch(action)通知store,reducer将接收到修改之前的state和action reducer更新state的副本,将新state返回给store- 使用
store的组件中通过store.subscribe(this.setState(store.getState()))订阅store来同步最新的store
为了提高代码健壮性和可维护性,把 action 单独声明为一个文件,并且把 action.type 声明为一个常量文件。
store
├── actionCreators.js // 生成action
├── actionType.js // action type对应的常量
├── index.js
└── reducer.js
- index.js
- actionCreators.js
- reducer.js
- actionType.js
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import reducer from './reducer';
const store = createStore(
reducer,
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
);
export default store;
import { INPUT_CHANGE } from './actionType';
export const changeInputAction = value => ({
type: INPUT_CHANGE,
value
});
import { INPUT_CHANGE } from './actionType';
const defaultState = {
todoText: ''
};
export default (state = defaultState, action) => {
if (action.type === INPUT_CHANGE) {
let newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state));
newState.todoText = action.value;
return newState;
}
return state;
};
export const INPUT_CHANGE = 'inputChange';
reducers函数的返回值要是可预测,也就是说里面不能写类似new Date,Ajax等的不可预测结果的代码
reducers不能修改原来的state,只能返回一个新的state,为了防止被误改造成bug,可以使用immutable.js来解决,它可以将state数据转化成一个特定的对象
npm i immutable redux-immutable -S
immutable对象通过get()和set()等 api 来操作数据,当有多个set()连用时可以使用merge({})来实现immutable通过fromJS可以将state转化成immutable对象,通过toJS()将immutable对象转化成js对象redux-immutable也提供了combineReducers,结合不同模块的reducers的同时还可以将state转化成immutable对象。
当项目越来越大时,项目中的 reducer.js 文件也会越来越臃肿,这个时候我们可以通过 redux
提供的combineReducers来将 reducer 拆分成不同的模块
import { combineReducers } from 'redux';
import mAReducer from '../mAReducer/store/reducer';
import mBReducer from '../mBReducer/store/reducer';
export default combineReducers({
A: mAReducer,
B: mBReducer
});
// 这样我们在使用mAReducer中的数据是就要通过state.A.xxx来获取其数据了
redux-thunk
中间件:位于 action 和 store 之间
redux-thunk 可以让 redux 使用异步操作
使用方式
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux';
import reducer from './reducer';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__
? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({})
: compose;
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(thunk));
const store = createStore(reducer, enhancer);
export default store;
例子
- actionCreators.js
- tab 组件使用
export const setTodoList = list => ({
type: GET_TODOLIST,
list
});
export const getTodoList = () => {
return dispatch => {
axios.get('http://localhost:8888/test/getTodoList').then(res => {
const todoList = res.data.datas;
const action = setTodoList(todoList);
dispatch(action);
});
};
};
componentDidMount() {
const action = getTodoList();
store.dispatch(action);
}
redux-saga
使用方式
- index.js
- actionCreators.js
- sagas.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux';
import reducer from './reducer';
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga';
import mySaga from './sagas';
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware();
const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__
? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({})
: compose;
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware));
const store = createStore(reducer, enhancer);
sagaMiddleware.run(mySaga);
export default store;
export const getSaga = list => ({
type: GET_SAGA,
list
});
import { takeEvery } from 'redux-saga/effects';
import { GET_SAGA } from './actionType';
function* getList() {
console.log('进行异步操作了');
}
function* mySaga(action) {
// 当dispatch的action.type = GET_SAGA时,调用getList方法
yield takeEvery(GET_SAGA, getList);
}
export default mySaga;
react-redux
使用 Provider 和 connect 实现 store 的共享,之前的写法是需要在需要使用 store 的组件中引入 store,并通过store.subscribe和store.getState来同步和获取最新的 store 内容。
<Provider store={store}>
{/* 包裹需要使用store的组件 */}
<App />
</Provider>
import { deleteTodoItemAction } from '../../store/actionCreators';
// 将store中的state的数据映射到组件的props中
const mapStateToProps = state => ({
...state
});
// 将dispatch映射到props中
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => {
return {
deleteTodoItem(index) {
const action = deleteTodoItemAction(index);
dispatch(action);
}
};
};
// Demo为需要使用store的组件
connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Demo);
hook
如果使用的是 hook 进行开发的话,可以使用 react-redux 提供的 hook api 来简化书写,并且不需要使用 connect() 来包裹组件,但是仍然需要使用Provider包裹父组件
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import { deleteTodoItemAction } from '../../store/actionCreators';
// 等同于前面的mapStateToProps
const counter = useSelector(state => state.counter);
const dispatch = useDispatch();
// 使用
dispatch(deleteTodoItemAction);
useSelector:返回 state 中的值,当一个action被dispatch时,useSelector会把之前的 selector 返回的结果和现在的结果进行浅比较(默认深比较===),如果不相同的话组件会被强制渲染,否则不会。
css 写法
react 不像 vue 那样可以优雅的在 vue 文件中写 css 代码,不过 react 也提供了几种 css 书写方式(待补充)
- css in js
- 使用 styled-components
- css-module(依赖于 webpack)
styled-components(使用 js 编写 css 代码)
- style.js
- 使用方式
import styled from 'styled-components';
export const Logo = styled.a.attrs({
href: '/'
})`
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
background: url(${props => props.imgUrl});
`;
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Logo } from './style';
class Header extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {};
}
render() {
return <Logo imgUrl="xxx" />;
}
}
export default Header;
上面这种写法等同于
render() {
return (
<a href="/" style={{position: "absolute", top: 0, left: 0}}></a>
);
}
react-router
npm i react-router-dom -S
import React from 'react';
import Header from './common/header';
import store from './store';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import Home from './pages/home';
import Detail from './pages/detail';
function App() {
return (
<Provider store={store}>
<Router>
<Header />
<Route path="/" exact component={Home}></Route>
<Route path="/detail" exact component={Detail}></Route>
</Router>
</Provider>
);
}
export default App;
exact 为精准匹配路由
页面跳转,使用 react-router-dom 中的 <Link to="xxx"></Link> ,重定向使用<Redirect to="xxx"></Redirect>
编程式写法:
this.props.history.(push()/goBack(num)/go()/replace())
<Route path="/post/:id" exact component={POST}></Route>
// POST组件通过this.props.match.params.id来获取id值
可以使用 withRouter 包裹组件来获取 history
React vs Vue
React 对比 Vue 来说,学习成本比较高,但是比较灵活。而 vue 提供了很多封装好的 api,学习起来对小白比较友好。